Ventilator: a machine that moves breathable air into and out of the lungs, to deliver breaths to patients who are physically unable to breathe, or breathe insufficiently. It is used to enhance or completely replace patient's ventilation in order to provide adequate oxygenation, reduce respiratory work and protect the lungs. Ventilator may be used either in invasive (intubation) or non-invasive way in cases such as respiratory failure, coma, suppression, burns, disorders of the central and peripheral nervous system, respiratory muscles and chest diseases that affect airways and alveoli.
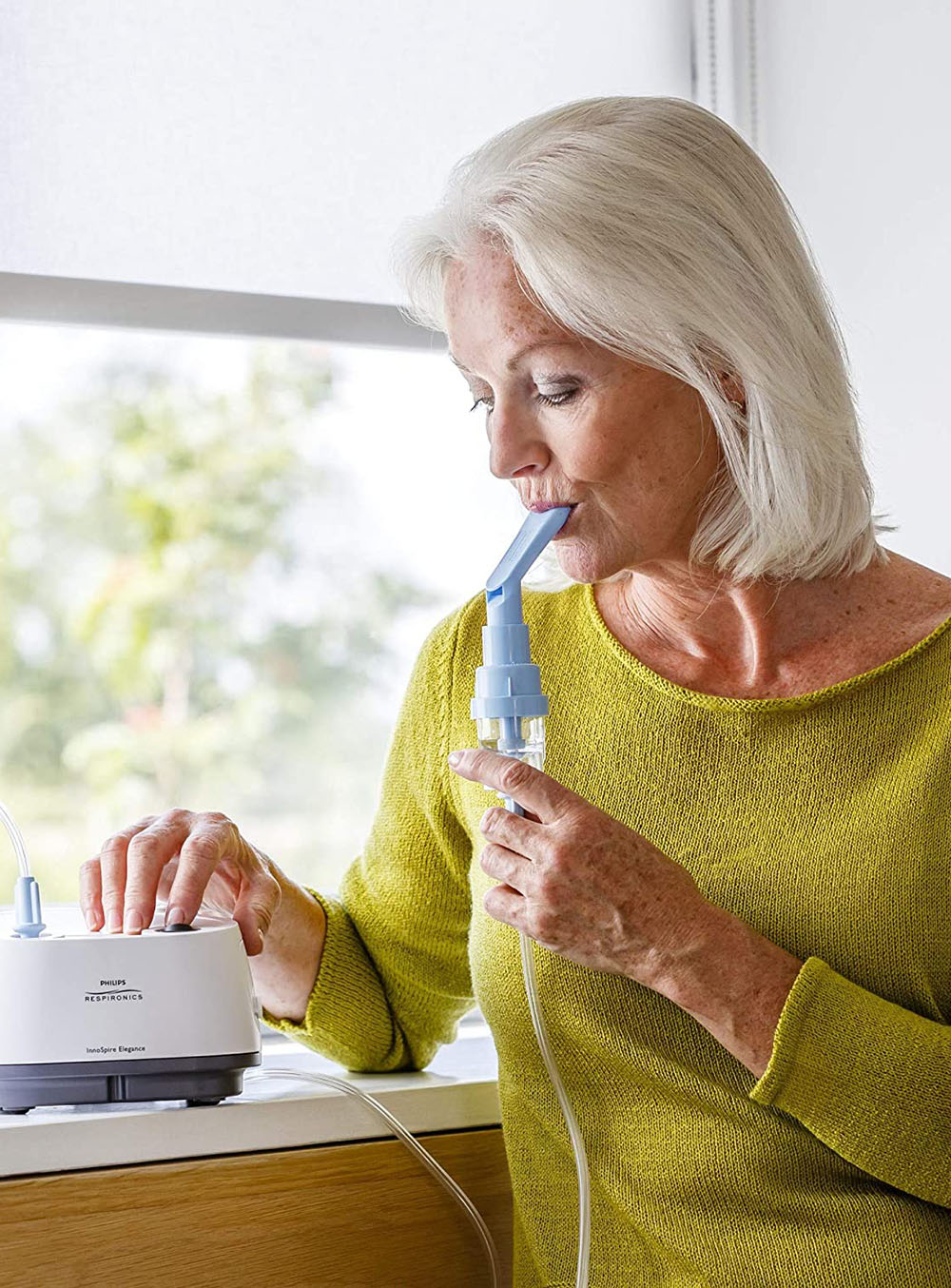
Suction: a device used for removing bronchial secretions to keep the airways clear of secretions, to avoid plugging of the airways and in order to facilitate breathing and for the prevention of infections and pulmonary aspiration. Suction is achieved through a special catheter and by applying negative pressure. Prerequisite: the inability of the patient to eliminate cough secretions.


