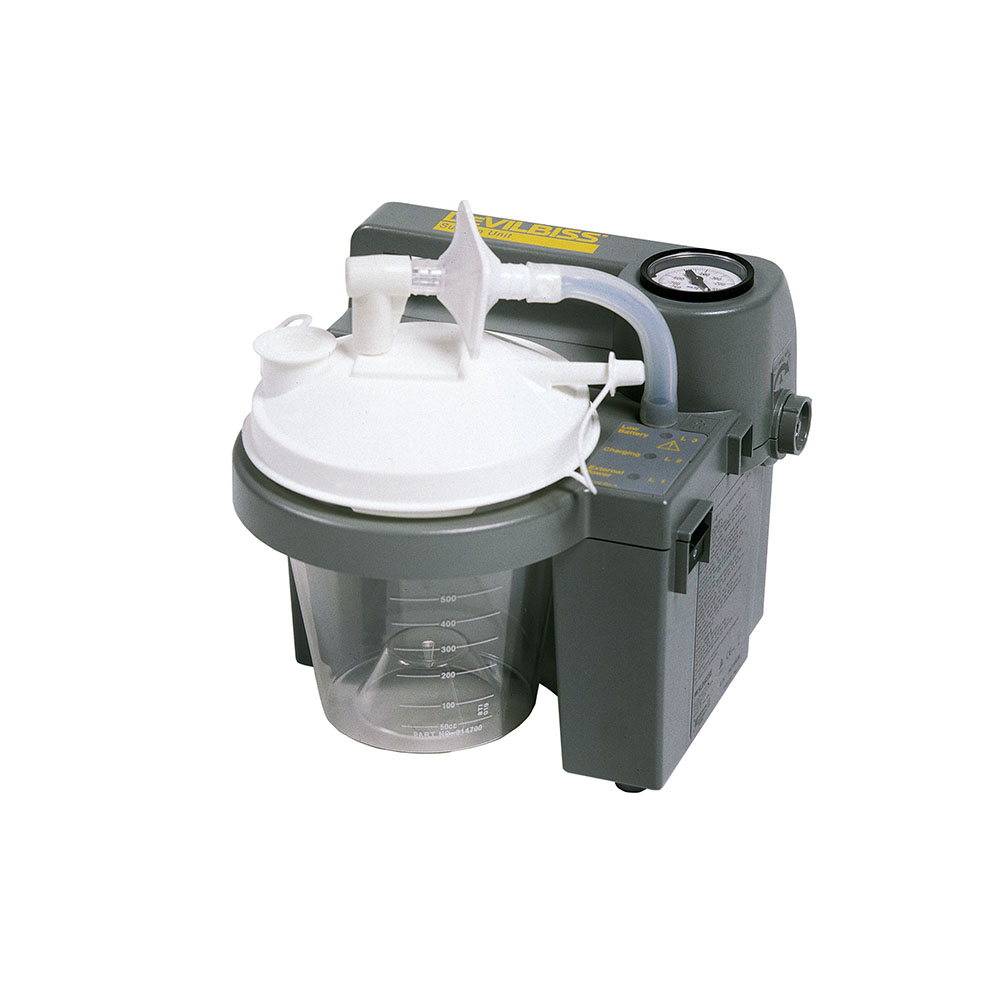
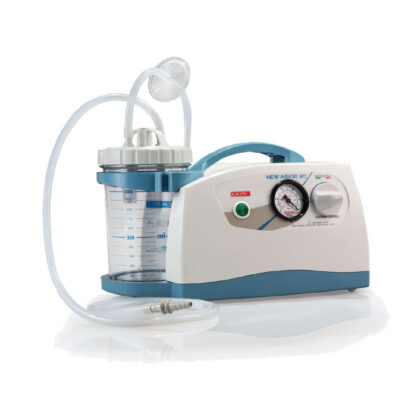
Αναρρόφηση Ρεύματος-Μπαταρίας DeVilbiss 7305 με επαναφορτιζόμενη μπαταρία
The DeVilbiss 7305 Series Homecare Suction Unit is a compact medical suctioning device which has been designed for reliable, portable operation. Because of the small size, light weight and DC operation, the DeVilbiss 7305 Suction Unit is ideal for providing suction in the home, or on the go with the DC cord. The 7305 P-D includes a rechargeable battery. Two collection bottle options give the choice between the standard 800 ml disposable canister and optional long-term reusable 1,200 ml canister.
The DeVilbiss 7305 Suction is a medical device with CE marking.
| Manufacturer |
|---|
720,00 €
- Vacuum adjustment allows for 80–550 mm Hg and a free flow of 27 liters/minute
- Meets American Association for Respiratory Care (AARC) guidelines for neonatal, infant, child and adult homecare suctioning
- Switch mode power supply allows operation on any AC voltage 100 V 240 V.
- Integrated bacterial filter
- Automatic float shut-off to prevent overflow into the unit
- Uses a rechargeable battery with 60 minutes run time
- Automatically recharges when connected to the power supply
- 12 V DC capability for vehicle charging
- Manufactured and tested to ISO10079-1:1999 Standard for Suction Equipment, achieving outstanding performance in the following tests:
- Electromagnetic Compatibility Test – VacuAide does not interfere with or is not susceptible to interference from other equipment such as ventilators
- Drop Test and Shock Vibration Test – VacuAide is far less likely to be damaged when dropped or shipped
- Excessive Temperature Test – VacuAide effectively works in a wide range of environmental temperatures
AARC Guidelines for appropriate sub atmospheric pressures:
- Neonates: 60 – 80 mm Hg
- Infants: 80 – 100 mm Hg
- Children: 100 – 120 mm Hg
- Adults: 100 – 150 mm Hg
Negative pressures should not exceed 150 mm Hg as higher pressures have been shown to cause trauma, hypoxemia and atelectasis.
Source: American Association for Respiratory Care. Nasotracheal suctioning 2004 revision and update. Respir Care 2004 Sep;49(9): 1080-4 (62 references).